

By Dr. Shehrebanu Merchant
What is Endometriosis?
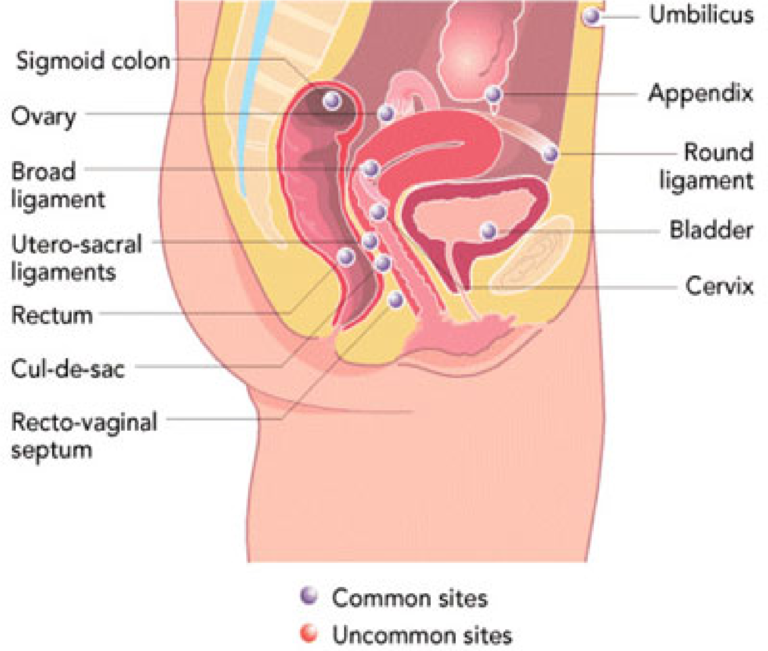
Endometrial cells usually line the inside of the uterus and these are the cells that are shed during menstruation. In Endometriosis, these endometrial cells that normally line the uterine cavity, grow outside of the uterus. This abnormal cell growth is called endometrial implants. The implants can attach in places such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, outside of the uterus or intestines, vagina or cervix. These implants are benign, or non-cancerous. It affects women in their reproductive years. The exact cause of endometriosis is not known.
Symptoms of Endometriosis
Most women do not have symptoms. The most common symptom women do have is pain, usually during menstruation and is relieved after menstruation. Some women have pain during intercourse, bowel movements or urination. The pain varies among women in intensity, in some women pain progresses while in others it resolves. Part of the pain depends on where the implants are located. Endometriosis can also cause infertility, most likely from both anatomical and hormonal reasons. Some other symptoms include lower back pain, diarrhea or constipation, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding, or blood in urine.
Treatment of Endometriosis
Medical
– NSAIDS such as ibuprofen or naproxen can relieve the pain and cramping, but have no effect on the endometrial implants.
– Oral Contraceptive Pills are commonly prescribed. If the pain is severe, women will often be told to take the pills consecutively, or skip the 7 sugar pills in the pack.
– Progestins used in high doses can also help. This may cause amenorrhea, or no menstrual periods. They also cause breast tenderness, bloating, weight gain, or irregular uterine bleeding.
– Gonadotropin releasing hormone analogs (Lupron) suppress regulatory hormones from the pituitary which causes a decrease in the estrogen produced by the ovaries. This mimics menopause and menstrual cycles stop. Possible side effects are vaginal dryness, hot flashes, irregular bleeding, and mood changes. Medications can be prescribed to relieve some of the side effects.
Surgical
– Conservative treatment is where the uterine and ovarian tissue is preserved, and is usually done by laparoscopy.
– Definitive treatment involves a hysterectomy, with or without the removal of the ovaries.
Treatment of Infertility
– Many women with mild to moderate endometriosis can still conceive without intervention. However, it may take longer to conceive.
– Decreased fertility is caused by both anatomical and hormonal reasons. Surgical intervention is usually preferred to resolve fertility issues.


Dr. Merchant is a board-certified obstetrician and gynecologist who has been practicing in the Northwest suburbs of Chicago for the last 27 years.
© Shehrebanu Merchant, MD | 2024 All Rights Reserved.